Before the 1930s, women gave birth to children in home settings assisted by traditional midwives. During this time, childbirth was a dangerous affair because many pregnant women and newborns lost their lives during or following childbirth (Corretti & Desai, 2018). However, during intrapartum, different intervention techniques can inhibit the risk, like the choice of instrument for operative vaginal delivery, maternal birthing position, perineal massage, application of warm compresses, episiotomy, and manual perineal support (MPS) (Gupta et al., 2017).
Labor is the process through which a fetus is delivered after 24 weeks of gestation. Labor begins when uterine contractions become consistent and cervical effacement and distention increase (Wahyuni et al., 2017). The first stage of labor occurs in two phases: the latent stage, the time taken for the cervix to open to 3 centimeters, and the active phase, which is the time taken from 3 centimeters to the complete opening of the cervix. During this stage of labor, the main problem is the failure to progress, which diagnosed if there is less than 2 centimeters dilatation in 4 hours or decelerating progress in parous women. Labor that is slow from the beginning is known as dysfunctional labor, whereas having sudden complications in previously progressive labor is referred to as arrest (Collins et al., 2008). Causes of unsatisfactory progress include inefficient uterine activity, malpresentation, or a large baby.
Our study's primary focus is that the second stage of labor encompasses the period between the full dilatation of the cervix and childbirth. The active part begins when the mother starts pushing using the abdominal muscles to “bear down.” Different positions may be used during this stage, such as standing, squatting, a supine position, or an all-fours pose (Pillitteri, 2010). On the other hand, the perineum may be complicated by the fetal head, expanding the anus as it comes down. Therefore, to support the perineum, a pad may be used to hold the perineum and shield the anus while the other hand conserves flexion, thereby regulating the head’s rite of passage, reducing perineal expansion, and minimizing tears (Geranmayeh et al., 2012). Delivery should occur within three hours of the second stage of labor in nulliparous women and two hours for multiparous women (Simkin et al., 2016).
During childbirth in the second stage, women could have a perineal trauma to the genitalia. The first-degree tear occurs spontaneously in the perineal skin; the second‐degree tear consists of the perineal muscles and skin; the third‐degree tears include the anal sphincter complex, and the fourth-degree tears include anal sphincter complex and anal epithelium (Fernando et al., 2015). Moreover, trauma may also result from prolonged pressure on the perineal nerve area during more prolonged childbirth labor (Akbarzadeh et al., 2016). The two classifications of perineal trauma: spontaneous perineal trauma or tear and episiotomy (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; Essa & Ismail, 2016).
The midwives and nurses should only consider episiotomies in specific situations, such as complicated vaginal delivery, breech, forceps, shoulder dystocia, and ventouse deliveries. A midwife or a nurse may also choose to perform an episiotomy when there are symptoms of fetal distress or signs that massive perineal trauma may occur. The indications of extensive perineal trauma include numerous perineal tears and perineal buttonholing (Oladapo et al., 2018). Moreover, perineal tears usually happen in women following vaginal childbirth that exert undue pressure on the perineum. It is classified into four groups depending on the extent of tissue damage. First-degree tears affect the skin around the perineum only, whereas second-degree tears damage the perineum and muscles. An episiotomy is an example of a second-degree tear. Third-degree perineal tears, on the other hand, involve damage to the anal sphincter complex. The three forms of third-degree tears are 3a, 3b, and 3c. In 3a tears, less than half of the external anal sphincter is destroyed, whereas 3b tears involve the destruction of more than half of the same anatomical area. In 3c tears, the internal anal sphincter is wrecked. Fourth-degree tears entail the destruction of the perineum, including the anal sphincter complex (internal and external) and the anal or rectal epithelium (Goh et al., 2018).
It appears that there is a relationship between the extent of perineal trauma and the effect on pain intensity. The highest reports of complaining due to perineal pain come from women who have third- or fourth-degree tears through the anal sphincter and rectal canal. Women with intact perineum have a low risk for infection, less blood loss, and less pain after childbirth. Most vaginal births are associated with tears or trauma in the perineal area (Aasheim et al., 2017). Midwives and nurses use various management techniques of the perineum, which play a significant role in reducing episiotomy and decreasing or minimizing perineal trauma. One of the most common is warm compresses (Moore & Moorhead, 2013).
Furthermore, a randomized controlled study by Essa and Ismail (2016) reported that pain intensity declined after warm compresses measured by VAS among the study group, and a strong significant effect was noticed on decreasing the episiotomy rate. In general, it is due to the potential treatment effects, including vasodilation, increased blood flow, tissue extensibility, muscle relaxation, and pain (Akbarzadeh et al., 2016). Studies in various parts of the world involving warm compresses during second-stage labor in nulliparous and primiparous women reported that it reduces the intensity of perineal pain. These findings were reported by Ibrahim et al. (2017) in Egypt, Baba et al. (2016) in Japan, and Ali et al. (2004) in Pakistan, among other countries.
However, many countries have not implemented significant beneficial practices. Instead, they uphold ineffective or deleterious practices. For example, routine procedures such as shaving of the pubic hair, episiotomy, seizures, electronic fetal monitoring, and intravenous (IV) infusion are commonly observed in some Saudi Arabia areas (Altaweli et al., 2014). The debate still occurs because some researchers recommended warm compresses (Essa & Ismail, 2016; Aasheim et al., 2017), while others found them to have limited or no benefits (Zare et al., 2014). The use of warm compresses to prevent or reduce the incidence and degree of perineal tear and pain is still controversial (Ibrahim et al., 2017). These contradictory results necessitate several studies to fill the gap in this respect. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the effect of warm compresses on perineal tear and pain intensity during the second stage of labor.
Methods
Study Design
This study applied a randomized controlled trial, post-test only design. The investigator allocates participants to an experimental or control condition on a random basis. So, this study tested if the independent variable, warm compresses, affected the dependent variables: perineal outcome and pain intensity.
Setting
Our study was conducted between 28 September 2018 to 30 October 2018 in King Khaled Hospital (KKH), affiliated with the Ministry of National Guard Hospital Affairs, King Abdulaziz Medical City – Western Region, Saudi Arabia. It is a 600 bedded Joint Commission International (JCI) accredited Tertiary level Hospital. The setting area for this experimental study was conducted in the labor and delivery (L&D) unit, which has six beds for delivery, three beds for induction of labor, and one room for operation room (OR). The patient characteristic and information attained from best care (medical record and patient).
Participants
All the primiparous pregnant women during the second stage of labor participated randomly in this study. The inclusion criteria include age from 18-35 years old, primigravida, healthy pregnancy, singleton pregnancy, cephalic presentation, full-term, and no contraindication for vaginal delivery. The exclusion criteria were multiple pregnant women, complicated labor, the coexistence of any medical or obstetrical risk factors, and pregnant women deliver a cesarean section.
The number of births in hospitals is estimated at 3000 births every year. The G*power software program (Faul et al., 2007) was used to calculate the sample size. The program allows sample size analyses and high-precision power. Besides, it computes the power values for sample size, effect size, and alpha levels. The aim was to achieve the power of 80% with effect size = 0.3, a err prob = 0.05, power (1-B err prob) = 0.80. The estimation was based on two tails a = 0.05. After calculation by G*Power, the sample size was 90 and added 10% for the dropped cases, with a total sample size of 100 primigravida pregnant women who met the inclusion criteria.
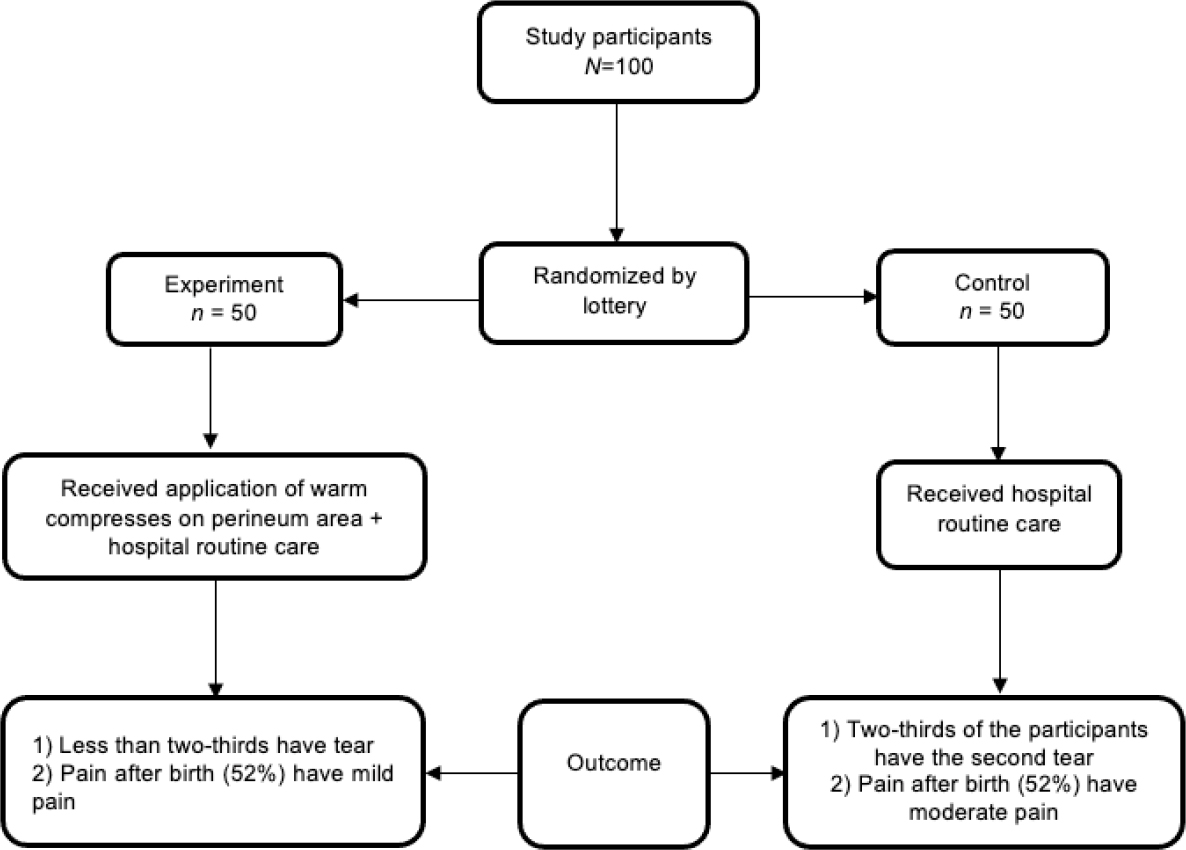
The investigator applied a simple random technique (lottery) through the participants' allocation into an experimental group or control group on a random basis. Each participant assigned the experiment by letter (A) and control by letter (B). Then paper folded and mixed inside a box, and the investigator asked one of the nurses to pick a number from the box. Then the participant was allocated to either the experimental group or control group (Figure 1). To avoid bias, the investigator divided the rooms for the control or experimental groups based on the women’s choices of the closed envelope. The experimental group room was numbered with an odd number, like 1, 3, and the control group's room was numbered with an even number like 2, 4,….etc.
Instruments
The instruments in this study consisted of 1) Sociodemographic Tool comprising socio-demographic characteristics including women's age and education level, occupation, previous admission to the hospital, reproductive history gestational weeks, number of prenatal care visits. The information is attained from medical records and patients; 2) Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) For Pain (Hawker et al., 2011). The investigator got permission to use the NRS tool for pain assessment. It ranged from zero pain to 10 severest pain in between the two extremity points equal distances measured 1cm as mild pain (1-2) moderate (3-4), severe (5-6), very severe (7-8), and severest pain (9-10). The NRS can be administered verbally or graphically for self-completion. The investigator asked the women to reveal a numeric value on the scale that best describes their pain degree scoring. The number that the women indicate to rate their pain intensity was recorded. The scores extend from 0–10; 3) Assessment Tool for Perineal Outcomes. It includes perineal outcome assessment questions in the form of an intact perineum, perineal tears degrees “first, second or third”, and episiotomy guided by the obstetrician diagnosis and previous studies (Farghaly et al., 2017; Lane et al., 2017).
All tools were tested for content validity by a jury of four experts in woman health nursing and one from the biostatistics field from the College of Nursing, King Saud Bin Abdul-Aziz University. A previous study also tested the reliability of the tool (Ibrahim et al., 2017). In addition, the second stage and perineal outcome assessment questionnaire were evaluated using Cronbach's Alpha coefficient test. The instrument contained relatively similar items, indicated high reliability, with an internal consistency of 0.81.
Before the primary data collection phase, the tools for the study were tested at National Guard in King Khaled Hospital, with ten patients. Those patients were not included in the main study. It took around one week to accomplish. The data were collected quickly with the interpretation of participant outcomes.
Intervention
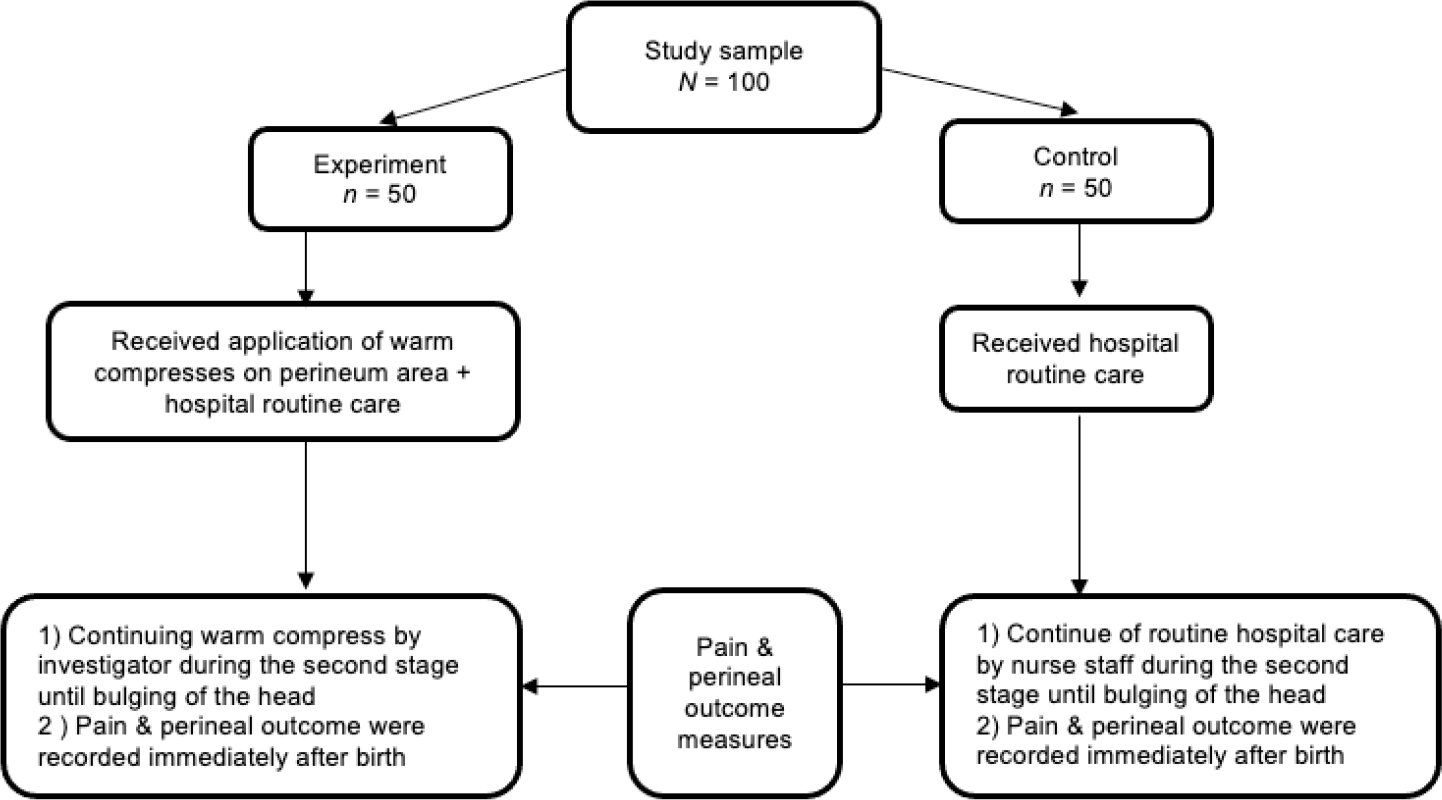
The control group received routine hospital care during the second stage of labor, such as half-hourly monitoring and documenting the frequency of contractions, assessing the vital signs, and checking the frequency of micturition or catheterization to evacuate the bladder. In addition, a vaginal examination was done after abdominal palpation without warm compresses.
The intervention group received routine hospital care in addition to the application of the warm compresses. First, the application of warm compresses was made through applying a sterile perineal pad (gauze) socked in warm water with a temperature range from 45C-59C measured by lotion thermometers, and the soaked each perineal pad was squeezed before being placed in the perineum area. Then the warm compresses are given continuously until bulging of the head (Figure 2).
Data Collection
The investigators collected data in the labor room between 23 August 2018 to 30 October 2018. The investigators directly observed, measured, and recorded the pain and perineal outcomes for both groups using the validated instruments. The participants were also asked to enumerate the severity of pain they have experienced after birth. A trained health member was assigned to assist the researcher in obtaining consent and interviewing the participants.
Data Analysis
SPSS program version 20 was used for statistical analysis. The variables are presented in the form of frequency and percentages, standard deviation, and mean. The Chi-square test was used to compete for categorical variables and test a significant difference between the study groups' outcome criteria. P-value was set at <0.05 for statistically significant criteria.
Ethical Consideration
Ethical approval in this study was obtained from the research unit committee at the College of Nursing, Jeddah, and from King Abdullah International Medical Research Center (KAIMRC) with approval number of IRBC/ 1711/18 on 27 September 2018. Prior to the study, each participant has signed informed consent. The investigators explained the nature of the study objectives and a clear explanation of data collection. Confidentiality was also ensured by explaining to the participants that all information was used only for research purposes and their identities were in the form of numbers, not names. In addition, the data collected could only be accessed by the investigators only. All participants also had the right to withdraw from the study at any time without penalty.
Results
Table 1 shows that the majority of the participants in this study aged between 23-26 years, 46% of the control group and 50% of the experimental group, respectively. The Chi-square test revealed no statistically significant difference in age between both groups (p = 0.918). In addition, more than half of them in both groups respectively graduated from university (55%), and there was no statistically significant difference in educational qualification (p = 0.864). The majority of the participants worked as housewives (75%) and lived in the urban areas (84%), and most of them had enough income per month (91%). There were no significant differences in occupation, current residence, and family income between the control and experimental groups (p > 0.05). It is noted that gestational age was similar because of the inclusion criteria of the participants (37-42) weeks, so it was not included in the table.
| Items | Control n (%) | Experiment n (%) | Total N (%) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | ||||
| 18-22 | 14 (28.0) | 14 (28.0) | 28 (28.0) | 0.918 |
| 23-26 | 23 (46.0) | 25 (50.0) | 48 (48.0) | |
| 27-30 | 10 (20.0) | 5 (10.0) | 15 (15.0) | |
| 31-35 | 3 (6.0) | 6 (12.0) | 9 (9.0) | |
| Educational qualification | ||||
| Primary school | 3 (6.0) | 3 (6.0) | 6( 6.0) | 0.864 |
| High school | 19 (38.0) | 20 (40.0) | 39 (39.0) | |
| Collegiate education | 28 (56.0) | 27 (54.9) | 55 (55.0) | |
| Occupation | ||||
| Working | 10 (20.0) | 8 (16.0) | 18 (18.0) | 0.261 |
| Housewives | 38 (76.0) | 37 (74.0) | 75 (75.0) | |
| Business | 2 (4.0) | 4 (8.0) | 6 (6.0) | |
| Any other specify (online business) | 0 | 1 (2.0) | 1 (1.0) | |
| Current residence | ||||
| Urban | 43(86.0) | 41 (82.0) | 84 (84.0) | 0.622 |
| Rural | 7(14.0) | 9 (18.0) | 16 (16.0) | |
| Family income/month | ||||
| More than enough | 0 | 2 (4.0) | 2( 2.0) | 0.743 |
| Just enough | 47 (94.0) | 44 (88.0) | 91 (91.0) | |
| Not enough | 3 (6.0) | 4 (8.0) | 7 (7.0) |
Table 2 shows that 28% of the total participants' gestational age was between 38 - 39 weeks. However, 6% of gestational age was 37 weeks. Regarding pelvic training, most participants did not attend any antenatal care classes (91%), and more than two-thirds of participants registered for seven visits during the pregnancy period (70%).
| Items | Control n (%) | Experiment n (%) | Total N (%) | Mean | Std. Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week of gestation | |||||
| 37 weeks | 2 (2.0) | 4 (4.0) | 6 (6.0) | 39.1 | 1.136 |
| 38 weeks | 11 (11.0) | 17 (17.0) | 28 (28.0) | ||
| 39 weeks | 16( 16.0) | 12 (12.0) | 28 (28.0) | ||
| 40 weeks | 13 (13.0) | 12( 12.0) | 25 (25.0) | ||
| 41 weeks | 8 (8.0) | 5 (5.0) | 13 (13.0) | ||
| Did you receive pelvic training | |||||
| Yes | 6 (6.0) | 3 (3.0) | 9 (9.0) | 1.91 | 0.287 |
| No | 44 (44.0) | 47 (47.0) | 91 (91.0) | ||
| Items | Median | IQR | |||
| Number of antenatal care visits | 7.00 | 7.00 | |||
Table 3 shows that two-fifth of the experimental group (40%) revealed lesser mild pain than the control group (52%). There was a statistically significant difference in mild pain in both groups (p = 0.001). In addition, more than half of the experimental group (52%) reported moderate pain than the control group (34%), and there was a statistically significant difference in moderate pain (p = 0.001). Also, a significant difference was found in severe pain (p = 0.001), which was higher in the control group (14%) than the experimental group (8%). There was no one having very severe or worst pain.
| Pain after birth | Control n (%) | Experiment n (%) | Total N (%) | df | Chi-square | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild pain (1,2) | 26 (52.0) | 20 (40.0) | 46 (46.0) | 4 | 54.6 | 0.001 |
| Moderate pain (3,4) | 17 (34.0) | 26 (52.0) | 43 (43.0) | 4 | 54.8 | 0.001 |
| Severe pain (5,6) | 7 (14.0) | 4 (8.0) | 11 (11.0) | 1 | 34.1 | 0.001 |
| Very severe (7,8) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 | ||
| Worst pain (9,10) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 |
Table 4 shows that there were significant differences in perineal condition between the experiment and control groups (p = 0.001), which the percentage of intact perineum was higher in the experimental group (22%) than in the control group (10%). In addition, those in the control group had a higher number of episiotomy (24%) than the experiment group (18%), and the majority of the control group (66%) and the experimental group (60%) had a perineal tear.
| Perineal Condition | Control n (%) | Experiment n (%) | Total N (%) | Chi-square | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intact | 5 (10) | 11 (22) | 16 (16) | 50 | 0.001 |
| Episiotomy | 12 (24) | 9 (18) | 21 (21) | 58 | 0.001 |
| Tear | 33 (66) | 30 (60) | 63 (63) | 38 | 0.001 |
Table 5 shows a significant difference in the degree of perineal tear in both groups (p = 0.043). However, the experimental group had lower degrees of perineal tear in the first, second, third degree than the control group.
| Degree of Perineal Tear | Control n (%) | Experiment n (%) | Total N (%) | Chi-square | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First degree | 13 (31.7) | 19 (61.3) | 32 (44.4) | 66.8 | 0.043 |
| Second degree | 24 (58.5) | 10 (32.3) | 34 (47.2) | ||
| Third degree | 4 (9.8) | 2 (6.5) | 6 (8.3) | ||
| Fourth degree | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
Discussion
Perineal injuries during childbirth may affect our goal to maintain perineal preservation, especially among primiparous women. Therefore, interventions for reducing perineal trauma and perineal pain are desirable. Midwives and nurses widely advocate warm compresses to reduce perineal trauma and improve comfort during the second stage of labor (Aasheim et al., 2017).
Our study aimed to assess the effect of warm compresses on the occurrence of perineal tears and pain intensity during the second stage of labor. The findings revealed that the follow-up measurement for pain intensity after birth in both the control and experimental groups with no statistically significant differences for pain score measurement at p = 0.175. These findings are supported by a study of Dahlen (2012) that examined pain intensity during the second stage of labor after warm packs. In this study, among women who received warm packs, their pain intensity score was less than those who received standard care. As such, women who had warm packs were significantly less likely to report lousy pain or the worst pain experienced at birth compared with women who received routine care without the application of warm packs. Also, our findings reported mild and moderate degrees of pain in the intervention group.
Furthermore, Dahlen (2012) examined the concepts of comfort and pain, including warm compresses' positive effects on reducing pain, and fewer women reported that the warm compresses helped to numb their perineum area. It seems that the warm compresses helped women to deal with the stinging sensation experienced in the perineum during the second stage of labor, also described by midwives as the “ring of fire.” Being able to get comfortable is a significant predictor of feeling in control during labor and birth.
Likewise, a study done by Ahmad and Turky (2010) found that pain scores were better for the women who used warm compresses compared to other women during the second stage at different points of time. This finding may reflect the benefit of using warm compresses through the second stage of labor. In addition, Akbarzadeh et al. (2016) reported that the warm compresses yielded significantly decreased pain during the second stage of labor by increasing blood flow to the damaged or inflamed area, which increased the elasticity of the collagen, which helps increase tissue flexibility and provide a good feeling and psychological convenience, which reduces the pain. In the same vein, warm compresses can relieve pain by enhancing blood circulation in the perineum (Ozgoli et al., 2016).
Regarding perineal tears, the results in this study revealed that the experimental group was better than the control regarding the intactness of the perineum. However, the experimental group had fewer perineal tears than the control group. Interestingly, the experimental group had fewer participants who received an episiotomy after childbirth than the control group. Further, the effect of warm compresses on different degrees of perineal tears reflected a statistically significant difference between both control and experimental groups at p < 0.043, with better outcomes for the experimental group than the control group in reducing the third degree of laceration and maintaining perineal integrity
Regarding stitches of the perineum, two previous randomized studies agreed with the current study indicated that warm compresses had no effects on the reduction of stitches in primiparous women, confirming the long-term effects of warm compresses (Dahlen, 2012). Likewise, Dahlen et al. (2009) support our findings, as no reduction was reported in perineal suturing after application of warm packs, and the trial was underpowered to assess third- and fourth-degree tear. Meanwhile, a study by Akbarzadeh et al. (2016) was not in line with our current research, reporting that a warm compress was effective in reducing the rate of episiotomy and the mean length of episiotomy incision, reducing pain intensity after childbirth and increasing the rate of an intact perineum, which indicates the significant effects of warm compresses on the reduction of lacerations and perineal trauma. Another study by Aasheim et al. (2017) also reported that midwives applied different techniques to decrease perineal trauma, genital trauma, episiotomy, pain intensity lubricant massage, and antenatal pelvic training. However, no studies declared the most effective method for reducing the laceration of the perineum during childbirth. Even though physiology literature has indicated that using a perineal pack during the second stage of labor leads to vasodilation, increased blood flow in the perineum area, increased relaxation, and increased muscle stretch, which was effective in pain transmission through reduction of nociceptive stimulation and improving comfort for pregnant women (Ozgoli et al., 2016).
Dissimilar to Essa and Ismail (2016), which was not in line with the present study’s results, revealing a significant reduction in episiotomy and vaginal/ perineal tear among the study group (p < 0.000). This finding may reflect the benefit of applying warm compresses on the perineum during the second labor stage. In addition, Mohamed et al. (2011) found that using a warm compress in the perineum area during the expulsive period reduces the occurrence of perineal laceration.
A study of Essa and Ismail (2016) has a dissimilarity with our study related to sample size, as theirs was more significant than the current study's. Besides, the perineal pad's material was different, as their study used a towel, but our study used a perineal pad made of gauze layers. Additionally, these findings boost the use of perineal warm compress by trained birth attendants, in line with the meta-analyses study by Aasheim et al. (2017), which found a significant effect of using warm compresses on third- and fourth-degree tears.
In the present study, findings revealed that warm compresses' application showed a reduction in third- and fourth-degree tears, reducing second-stage perineal trauma in primiparous women. In the same vein, Aasheim et al. (2017) also found that warm compresses and massage may reduce severe perineal trauma and third- or fourth-degree tears. Hands‐off techniques may decrease the number of episiotomies, but it was not clear that they had a valuable effect on other perineal trauma.
Many advantages occur from applying warm compresses that produce relaxation by reducing muscle spasms and reducing pain intensity during childbirth. This study reflects the benefit of using warm compresses to decrease the perineal trauma, which is evident by reducing the second and third-degree tear rate in the experimental group compared with the control group. Therefore, all governmental/educational hospitals should provide effective planned in-service training programs for maternity nurses regarding warm compresses' advantages during the second stage of labor. Further research is required to assess the effect of warm compresses on multiparous women relating to receiving the same benefit of comfortable and relief pain degree during the second stage of labor integrating with assessing woman's satisfaction regarding the use of warm perineal compresses during the second stage of labor.
The limitation of the study might include: First, eligible participant criteria as primiparous women lead to difficulty collecting data within the determined time of data collection. Second, most participants showed satisfaction regarding warm compresses, but the satisfaction variable was not included in this study.
Conclusion
This study concluded that the application of warm compresses during the second stage of labor has better effects on perineal outcomes. In addition, it showed evidence of other benefits regarding the positive effect on reducing the second and third-degree of perineal tear and pain intensity to lower pain degrees within the experimental group. Therefore, the practice of applying warm perineal compresses in the second stage of labor is highly acceptable by mothers and midwives or nurses in helping to reduce perineal pain and increase comfort. Furthermore, the finding reveals that the experimental group that experienced intact perineum reducing tear and pain is better than the control group. Interestingly, the experimental group lesser episiotomies compared to the control group.